Development boosts Xinjiang's business edge

TIMELINE
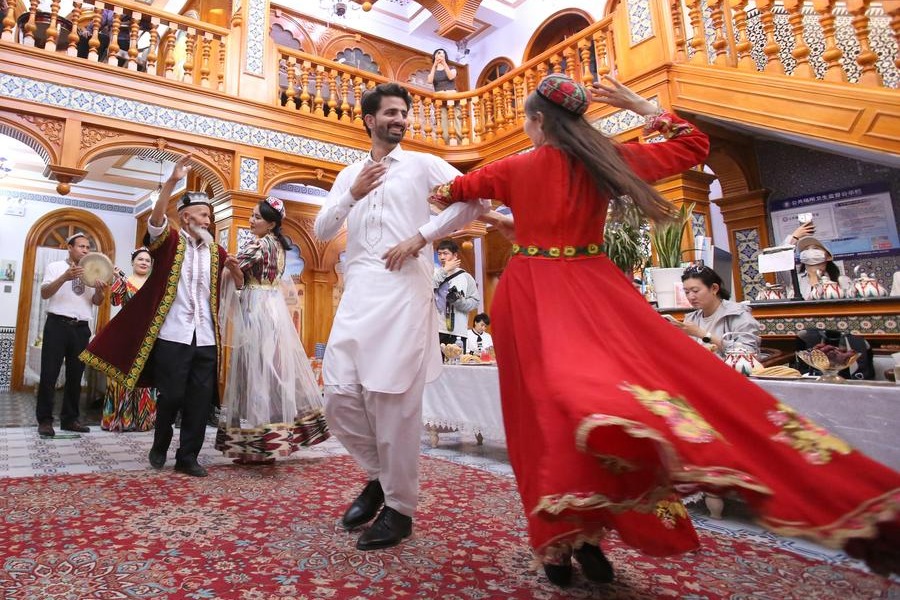
September 2012: The second China-Eurasia Expo is held in Urumqi, capital of the Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region. It is a platform to further expand areas of cooperation across Eurasia. In a congratulatory letter to the opening of the seventh expo this year, President Xi Jinping says Xinjiang has fully leveraged its geographical strengths and proactively developed itself into a core area of the Silk Road Economic Belt.
2014: A series of anti-terrorism and deradicalization measures are introduced to achieve long-term peace in the Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region. On Dec 26, the Lanzhou-Xinjiang High-speed Railway begins operations. As the first long-distance high-speed line in China's western regions, it connects Lanzhou, capital of Gansu province, with Urumqi.
2016: At the end of the year, the authorities announce that there have been no terrorist cases or incidents in the region since the anti-terrorism and deradicalization measures came into force in 2014.
2020: By the end of the year, more than 2.7 million rural people in Xinjiang living below the poverty line are lifted out of poverty, and 3,666 villages and 32 counties are no longer officially classified as "poor".
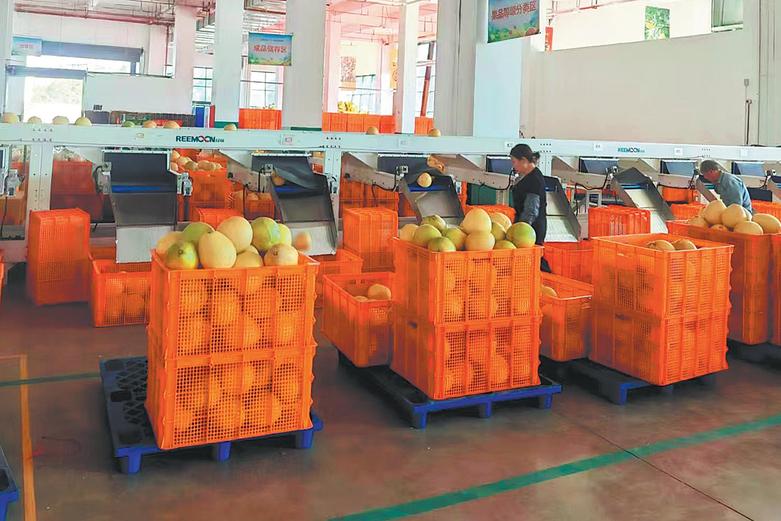
2021: Regional GDP reaches 1.6 trillion yuan ($222 billion), double the figure in 2012. Despite the ongoing COVID-19 epidemic, Xinjiang receives 191 million tourist visits, a year-on-year rise of 20.5 percent.
2022: By the end of the year, the region is set to be home to 25 airports — rising from the 17 registered in 2010 — the largest number of such facilities among China's provincial-level areas.
- Commercial Aerospace Forum spotlights innovation, space exploration programs
- Investigation underway after search completed in fire-hit buildings in Hong Kong
- Linyi sets sail for Africa to forge strong ties
- Xi holds talks with Macron
- Xi holds welcome ceremony for Macron
- Senior Chinese official stresses improving system for narcotics control